Categories:
News
Research
Industrial Automation
Automation Components
Electric Components
Robots
Artifint
New Wave
Motors
Practical
News
Research
Industrial Automation
Automation Components
Electric Components
Robots
Artifint
New Wave
Motors
Practical
Tags:
announcement, website, testing, PLC rack, I/O, Cable, Parallel communication, Serial communication, ASCII, RS232, RS-232 Communication, ProfiBus, Industrial robots, manipulator, Cartesian robot, SCARA Robot, Articulated robot, end-of-arm-tooling, Robotics, Metalcasting, automotive industry, Integrated force sensing, shunt, electric current, Human - Machine Interface, HMI, MMI, Human Factors Engineering, Usability Engineering, User Interface, Systems Engineering, Opton, T-WIN20, T-WIN20 KDM, robot bender, pipes, PROFIBUS, Process Field Bus, communication, automation technology, PROFINET, Industrial Ethernet, Central Association for the Electrical Industry, ZVEI, PROFIBUS FMS, PROFIBUS DP, PROFIBUS International, field-bus, OSI Network model, Field bus Data Link, FDL, RS485, fiber-optic transmission, Manchester Bus Power, MBP, bus topology, Fieldbus Message Specification, Decentralized Periphery, PROFIBUS PA, PROFIdrive, PROFIsafe, The PROFIBUS User Organization, Contactor, Relay, Differences, automation, switch, power contacts, auxiliary contacts, contact springs, electromagnet, coil, armature, Grounding, shielding, EMI, Shields, PWM, RF signal, Magnetic coupling, Pulse-width-modulation, PWM simulation, EMI noise, CE mark, and many more...
PROFIBUS
 PROFIBUS (Process Field Bus) is a standard for field bus communication in automation technology and was first promoted in 1989 by BMBF (German department of education and research)
and then used by Siemens. It should not be confused with the PROFINET standard for Industrial Ethernet. PROFIBUS is not one communication system, but a variety of protocols built
on the same field-bus technology bundle. Users can combine varieties of PROFIBUS protocols with their own software and other requirements, resulting in a unique application profile.
With many profiles available, PROFIBUS can suit specific needs. One thing remains the same, though. Through thorough testing, PROFIBUS devices meet a high standard of quality befitting a high quality network.
PROFIBUS (Process Field Bus) is a standard for field bus communication in automation technology and was first promoted in 1989 by BMBF (German department of education and research)
and then used by Siemens. It should not be confused with the PROFINET standard for Industrial Ethernet. PROFIBUS is not one communication system, but a variety of protocols built
on the same field-bus technology bundle. Users can combine varieties of PROFIBUS protocols with their own software and other requirements, resulting in a unique application profile.
With many profiles available, PROFIBUS can suit specific needs. One thing remains the same, though. Through thorough testing, PROFIBUS devices meet a high standard of quality befitting a high quality network.History
PROFIBUS was born out of a combined push by the German government, German companies, and other industry leaders in the late 1980s. Their effort created an automation solution that is not only still viable today, but has led to further solutions. The proud heritage of PROFIBUS allows for many European customers to turn to automation specific to their needs.
Origin
In 1987, 21 companies and institutions in Germany joined forces to create a new protocol. Their goal was to create a bit-serial Fieldbus system. In order for the system to be viable, they needed to standardize the field device interface. The group, which had taken the name Central Association for the Electrical Industry (ZVEI), completed its goal with the creation of PROFIBUS FMS (Fieldbus Message Specification).
This new protocol satisfied standardization of Industrial Automation through a protocol capable of sending complex communications. The ZVEI was not finished, though. In 1993, the group introduced a new standard, PROFIBUS DP (Decentralized Periphery). This new version featured more simplicity, including easier configuration and faster messaging.
The ZVEI continues serving the electronics industry in Germany. Their work to create PROFIBUS was vital.
Organizations
PROFIBUS standards are maintained and advanced via a pair of important organizations. In 1989, PROFIBUS manufacturers and users created the PROFIBUS User Organization (PNO). This group was, and still is, a non-commercial venture. Members work to advance PROFIBUS through support and education, including publishing documents that help users satisfy their needs using existing technology.
A larger group was formed in 1995 and named PROFIBUS International, or PI. As the largest Fieldbus user association in the world, PI is able to undertake many tasks vital to the progression of PROFIBUS. Like the PNO, PI educates users on PROFIBUS and helps advance its placement throughout the world. The organization goes further, though, by helping with quality assurance, setting standards, and developing new PROFIBUS technologies.
Overview
PROFIBUS is a smart, field-bus technology. Devices on the system connect to a central line. Once connected, these devices can communicate information in an efficient manner, but can go beyond automation messages. PROFIBUS devices can also participate in self-diagnosis and connection diagnosis. At the most basic level, PROFIBUS benefits from superior design of its OSI layers and basic topology.
OSI Model
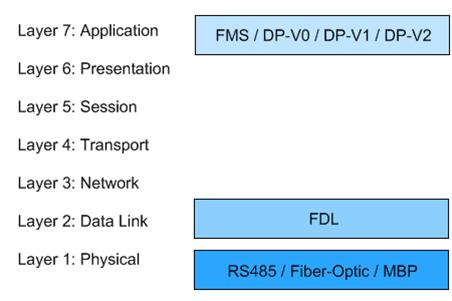 PROFIBUS networks make use of three separate layers of the OSI Network model. First, PROFIBUS describes the application layer. There are multiple versions of PROFIBUS that handle different
types of messaging at the application layer. Some of the types of messaging PROFIBUS supports include cyclic and acyclic data exchange, diagnosis, alarm-handling, and isochronous messaging.
PROFIBUS networks make use of three separate layers of the OSI Network model. First, PROFIBUS describes the application layer. There are multiple versions of PROFIBUS that handle different
types of messaging at the application layer. Some of the types of messaging PROFIBUS supports include cyclic and acyclic data exchange, diagnosis, alarm-handling, and isochronous messaging.PROFIBUS does not define layers three through six. It does, however, define the data link and physical layers, layers one and two. The data link layer is completed through a Field bus Data Link, or FDL. The FDL system combines two common schemes, master-slave methodology and token passing. In a master-slave network, masters, usually controllers, send requests to slaves, sensors and actuators. The slaves respond accordingly. PROFIBUS also includes token passing, a system in which a "token" signal is passed between nodes. Only the node with the token can communicate. The token passing concept is like the speaking conch; only the person with the conch is allowed to talk.
Finally, PROFIBUS defines a physical layer, though it leaves room for flexibility. PROFIBUS systems can have three types of media. The first is a standard twisted-pair wiring system, in this case RS485. Two more advanced systems are also available. PROFIBUS systems can now operate using fiber-optic transmission in cases where that is more appropriate. A safety-enhanced system called Manchester Bus Power, or MBP, is also available in situations where the chemical environment is prone to explosion.
Topology
PROFIBUS uses the bus topology. In this topology, a central line, or bus, is wired throughout the system. Devices are attached to this central bus. One bus eliminates the need for a full-length line going from the central controller to each individual device.
In the past, each PROFIBUS device had to connect directly to the central bus. Technological advancements, however, have made it possible for a new "two-wire" system. In this topology, the PROFIBUS central bus can connect to a ProfiNet Ethernet system. In this way, multiple PROFIBUS busses can connect to each other.
Types of PROFIBUS
PROFIBUS has advanced through a handful of revisions. In some cases, advances have led to a new type of PROFIBUS. In other cases, new revisions mean different versions of the same type of PROFIBUS. In any case, the variety of PROFIBUS solutions mean the system can be adapted to fit the varying needs of different industries.
PROFIBUS FMS
The initial version of PROFIBUS was PROFIBUS FMS, Fieldbus Message Specification. PROFIBUS FMS was designed to communicate between Programmable Controllers and PCs, sending complex information between them. Unfortunately, being the initial effort of PROFIBUS designers, the FMS technology was not as flexible as needed. This protocol was not appropriate for less complex messages or communication on a wider, more complicated network. New types of PROFIBUS would satisfy those needs. PROFIBUS FMS is still in use today, though the vast majority of users find newer solutions to be more appropriate.
PROFIBUS DP
The second type of PROFIBUS is more universal. Called PROFIBUS DP, for Decentralized Periphery, this new protocol is much simpler and faster. PROFIBUS DP is used in the overwhelming majority of PROFIBUS application profiles in use today. Application profiles allow users to combine their requirements for a specific solution, and they will be discussed in more detail shortly. PROFIBUS DP has, itself, three separate versions. Each version, from DP-V0 to DP-V1 and DP-V2, provides newer, more complicated features.
PROFIBUS PA
PROFIBUS PA is a protocol designed for Process Automation. In actuality, PROFIBUS PA is a type of PROFIBUS DP Application profile. PROFIBUS PA standardizes the process of transmitting measured data. It does hold a very important unique characteristic, though. PROFIBUS PA was designed specifically for use in hazardous environments.
In most environments, PROFIBUS PA operates over RS485 twisted pair media. This media, along with the PA application profile supports power over the bus. In explosive environments, though, that power can lead to sparks that induce explosions. To handle this, PROFIBUS PA can be used with Manchester Bus Powered technology (MBP).
MBP Technology
The MBP media was designed specifically to be used in PROFIBUS PA. It permits transmission of both data and power. The technology steps the power down, though. A smaller power reduces, or nearly eliminates, the possibility of explosion. Buses using MBP can reach 1900 meters and can support branches.
Application Profiles
 PROFIBUS can be tailored to specific needs using application profiles. Profiles are pre-defined configurations of the functions and features available from PROFIBUS for use in specific devices or applications.
They are specified by PI working groups and published by PI. Profiles are important for openness, interoperability and interchangeability, so that the end user can be sure that similar equipments from different
vendors perform in a standardised way. User choice also encourages competition that drives vendors towards enhanced performance and lower costs.
PROFIBUS can be tailored to specific needs using application profiles. Profiles are pre-defined configurations of the functions and features available from PROFIBUS for use in specific devices or applications.
They are specified by PI working groups and published by PI. Profiles are important for openness, interoperability and interchangeability, so that the end user can be sure that similar equipments from different
vendors perform in a standardised way. User choice also encourages competition that drives vendors towards enhanced performance and lower costs.There are PROFIBUS profiles for Encoders, Laboratory instruments, Intelligent pumps, Robots and Numerically Controlled machines, for example. Profiles also exist for applications such as using HART and wireless with PROFIBUS, and process automation devices via PROFIBUS PA. Other profiles have been specified for Motion Control (PROFIdrive) and Functional Safety (PROFIsafe). There are many profiles that combine standards for transmission media, communication protocol (FMS, DP-V0, etc...), and unique protocols. Each application profile is tailored to a specific use, and new profiles appear regularly. To list them all would be cumbersome.
PROFIsafe
PROFIsafe uses additional software to create a high-integrity network. This network is useful in situations where high safety is a requirement. For suppliers and manufacturers to be certified in PROFIsafe, they must maintain high standards in quality.
PROFIdrive
PROFIdrive was created for motion control applications. Software added to the PROFIBUS DP specification allows the network to achieve precise control of servo motors and other equipment. Thus PROFIdrive can achieve synchronization across the network.
Quality Assurance
The PROFIBUS User Organization has created a conformance testing program to ensure devices meet high standards. In this program, a device is sent to an independent laboratory for testing. The device then undergoes a comprehensive series of tests, including Hardware, Conformity, and Function tests, among others. The test results are documented
When a device passes all tests, its manufacturer can apply for a conformance certificate. The certificate is valid for three years and can be renewed with further testing.
More info on:
www.rtaautomation.com/profibus/
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Profibus
This post belongs to category: